Volume 81, Issue 2
Displaying 1-50 of 56 articles from this issue
-
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 1-16
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
DOIhttps://njjn-jsjc-gov-cn-s-1416.res.gxlib.org.cn:443/rwt/1416/https/MSYXTLUQPJUB/10.11641/pde.81.2_1Download PDF (10252K)
-
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 39-43
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (755K)
-
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 44-47
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (779K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 48-52
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (335K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 53-56
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (253K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 57-61
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (966K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 62-66
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (997K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 67-71
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (429K)
-
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 72-73
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (183K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 74-75
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (238K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 76-77
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (288K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 78-79
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (384K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 80-81
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (423K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 82-83
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (455K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 84-85
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (566K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 86-87
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (443K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 88-89
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (341K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 90-91
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (305K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 92-93
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (330K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 94-95
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (266K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 96-97
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (629K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 98-99
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (605K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 100-101
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (167K) -
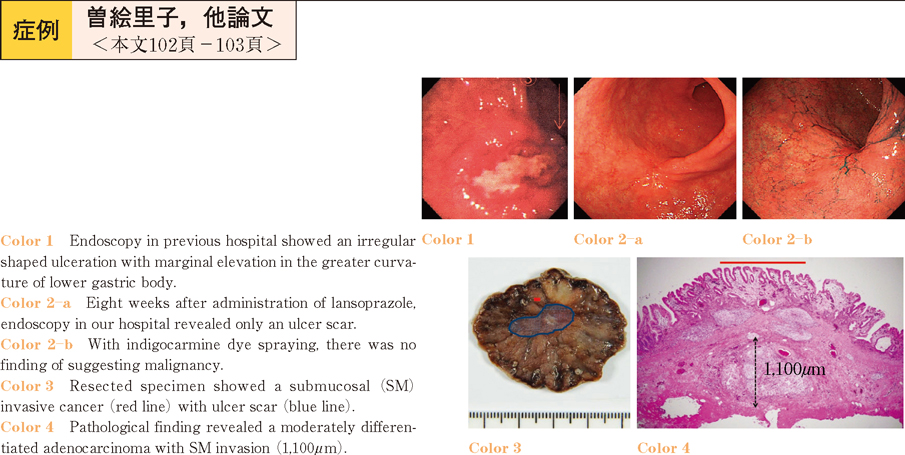
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 102-103
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (232K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 104-105
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (398K) -
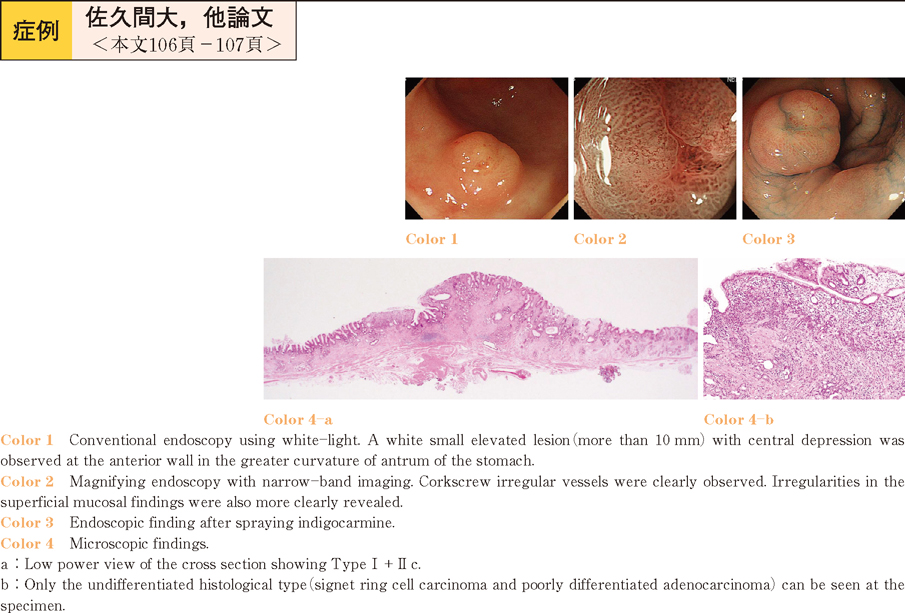
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 106-107
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (224K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 108-109
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (276K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 110-111
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (729K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 112-113
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (208K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 114-115
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (228K) -
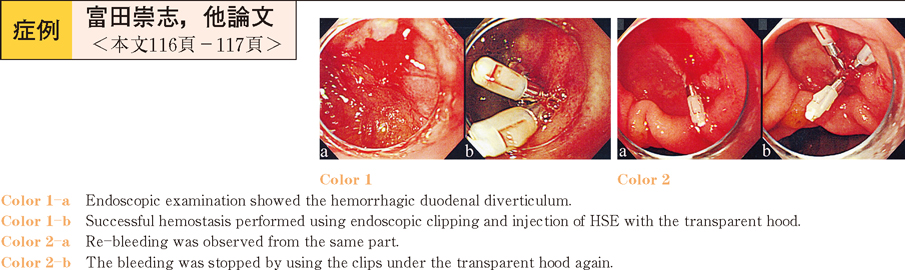
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 116-117
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (216K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 118-119
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (455K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 120-121
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (398K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 122-123
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (376K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 124-125
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (337K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 126-127
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (351K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 128-129
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (387K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 130-131
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (447K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 132-133
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (449K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 134-135
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (447K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 136-137
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (292K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 138-139
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (415K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 140-141
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (186K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 142-143
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (402K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 144-145
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (539K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 146-147
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (340K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 148-149
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (322K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 150-151
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (445K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 152-153
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (405K) -
2012 Volume 81 Issue 2 Pages 154-155
Published: December 07, 2012
Released on J-STAGE: March 06, 2013
Download PDF (445K)